- Types of machining: cutting, welding, structuring, marking
- Machined materials: steel, titanium, plastics
- Purpose of machining: clean, smooth surfaces, achieving complex shapes with small overall dimensions, pore-free welds, creating microchannels, product identification
- Adventages: high cleanliness and edge quality, minimal heat affected zone, contactless process, cutting any shape, no finishing, small heat affected zone, high strength of joints
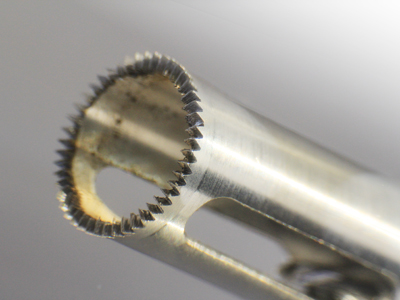
Medical devices, including implants and stents, must be of the highest quality, as they are placed in the human body and provide the body with proper function. This translates directly into the requirements for their manufacturing process, among which the most important are cleanliness, smoothness of surfaces and absence of pollen and dirt. Such stringent criteria make the laser the ideal tool for processing materials for medical purposes – both cutting and welding. This is because this device offers high edge quality, a minimal heat affected zone and a non-contact process.
Cutting
Laser cutting provides high surface smoothness with minimal burrs, so no additional post-processing is required. In addition, the high ease of beam guidance allows the cutting of complex shapes even on cylindrical surfaces, which is used in the production of stents and needles. Such manufacturing is faster and more precise compared to conventional techniques, such as mechanical or chemical machining. Lasers also allow processing of any material – from stainless steel to titanium to plastics.
Welding
Laser welding offers the highest quality welds free of defects and porosity, due to the high speed and precision of the beam guidance. The resulting joints are clean and sterile, as no additional finishing is required. Among the materials used in medicine are titanium alloys, including shape memory materials. Due to the small heat-affected zone during bonding, these materials do not lose their original properties and no deformation occurs.
A wide range of thermosetting and thermoplastic materials used in medicine for the manufacture of probes, endoscopes or catheters, among others, can also be laser bonded to another material, creating perfectly tight joints. And by properly controlling the laser power, the strength of the component is not affected.
Structuring
Laser micromachining techniques include a method called structuring. It is a development of the laser ablation process, which involves the removal of a layer of material. By selectively controlling the ablation process, it is possible to obtain microchannels on the surface, which are particularly useful in the manufacture of medical implants. Their presence increases the interaction of the component with the human body, and thus the growth of tissues on the previously modified outer layer, which provides greater biocompatibility of the material.
Marking
Laser technology offers many different methods for marking parts – depending on the type of material used. For example, in the case of stainless steel, laser annealing is most commonly used. Marks and codes applied in this way are created by changing the color of the surface without removing the top layer of the material, so the product remains sterile and clean.
Laser engraving, on the other hand, makes it possible to quickly create lettering and symbols even on very small surfaces while maintaining high part legibility. The ease of automation means that the laser can become an integral part of the production line and mark parts on the fly – even at high operating speeds.
