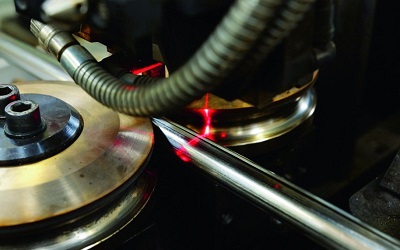
Effects of eye and skin exposure to laser radiation
| Radiation range | Eye | Skin |
|---|---|---|
| 180-400 nm | photochemical and thermal damage to the cornea and lens | erythema |
| 400-700 nm | photochemical and thermal damage to the retina | uszkodzenia termiczne |
| 700-1400 nm | thermal damage to the cornea, retina and lens | thermal injuries |
| 1400-2600 nm | thermal damage to the cornea, retina and lens | thermal injuries |
| 2600 nm-1 μm | thermal damage to the cornea, retina and lens | thermal injuries |
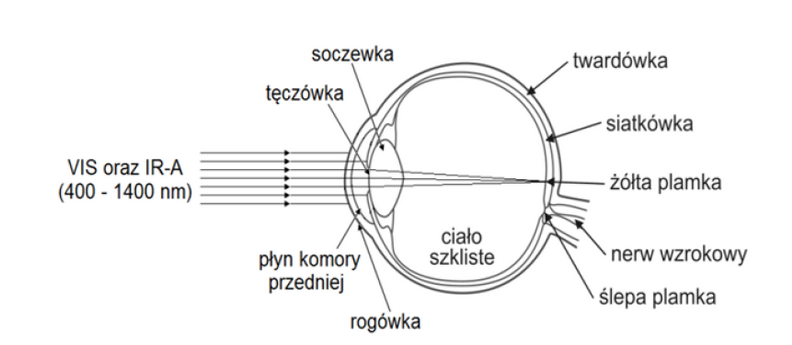
Effects of laser radiation on the eyeball
| Classes of lasers and laser devices (according to PN-EN 60825-1:2014:11) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Laser radiation completely safe in all conditions | |
| 1M | Emission of radiation in the region of λ = 302.5 ÷ 4000 nm, safe provided that optical elements (such as lenses) are not used | |
| 2 | Emission of radiation in the area of λ = 400 ÷ 700 nm, safe provided there is no direct exposure to the eye | |
| 2M | Radiation emission in the region of λ = 400 ÷ 700 nm, safe as long as there is no direct exposure to the eye and optical elements are not used | |
| 2M | Radiation emission in the region of λ = 302.5 ÷ 106 nm, safety glasses required | |
| 3B | Lasers absolutely dangerous with direct exposure to the eye and sometimes to the skin, safe to look at diffuse radiation | |
| 4 | Radiation emission hazardous to eyes and skin under all conditions, can cause fire or explosion | |
It is the laser manufacturer’s responsibility to mark the class of laser and to provide operating instructions that take into account the appropriate selection of protective equipment. However, the precautions taken by the company’s management play an equally important role.
The first step in this case should be the preparation of a detailed risk assessment that takes into account the basic parameters of the laser device, as well as all types of hazards posed by the laser. After all, in addition to radiation exposure, it can generate electrical, vapor and gas, fire and explosion hazards, as well as those associated with associated radiation (non-laser, such as X-rays). The guide “Artificial Optical Radiation – Principles of Occupational Risk Assessment,” available from the Central Institute for Labor Protection, can help in making a proper assessment.
The basic guidelines and recommendations for laser users in the table below may be of additional help.
Basic requirements and recommendations for users of laser equipment by laser class
| Requirements and recommendations | 1 do 2M | 3R | 3B | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appointment of laser safety inspector | • | • | • | |
| Use of remote locking switch | • | • | ||
| Key startup | • | • | ||
| Use of a laser beam limiter or attenuator | • | • | ||
| Radiation emission signaling device | • | • | • | |
| Use of warning signs | • | • | • | |
| Shielding of laser beams | • | • | • | |
| Avoiding mirrored reflections | • | • | • | |
| Use of personal eye protection equipment | • | • | ||
| Use of protective clothing | • | • | ||
| Safety training for workers on working with lasers | • | • | • |